Lecture 5: Operating System Security Authentication and Access Control
TK
Athicha Leksansern
26 มกราคม 2567
 Chipi Chipi
Chipi ChipiSecurity in Operating System
- Operating System
- โปรแกรมที่บริหารจัดการ Resource ของระบบ
- ป้องกันไม่ให้ ผู้ใช้งานอีกคนเข้าถึงผู้ใช้งานอีกคน
- ป้องกันไม่ให้พื้นที่ใน Memory หรือ Storage ที่สำคัญ ถูกเขียนทับ โดย Unauthorized proceses
- ทำ Identification และ Authentication สำหรับการใช้งาน Remote
- มั่นใจว่า Reousrce ถูกแบ่งใช้งานอย่าง fair
Security-relevant features
- Enforced sharing: Resource จะถูกแบ่งให้ users อย่างถูกต้อง
- Interprocess communication and synchronization: OS จะเป็นตัวกลางในการสื่อสารระหว่าง process
- Protection of critical operating system data: OS จะต้องป้องกันพื้นที่ของไฟล์ OS
- Guaranteed fair service: การแบ่ง CPU scheduling จะ fair
- Interface to hardware
- User authentication: OS จะระบุ users ที่ต้องการใช้งานได้
- Memory protection
- File and I/O device access control
- Allocaion and access control to general objects
Security Methods of OS
- ง่ายที่สุดคือการ Separation หรือ การแบ่ง Objects ของอีกคน กับอีกคน
- Physical separation: คนละเครื่อง
- Temporal separation: one at a time
- Logical separation: OS จำกัดไม่ให้โปรแกรม เข้าถึงส่วนอื่นๆ ที่ถูกกำหนดไว้
- Cryptographic separation
- บางครั้ง users อาจจะต้องการ share resources
- OS จะอณุญาติให้ share แบบ flexible sharing
- Public object: สามารถเข้าถึงได้ทุกคน
- Private object: สามารถเข้าถึงโดยเจ้าของเท่านั้น
Memory Protection
- Fence: จะเป็นพื้นที่ที่ OS กำหนดไว้ ว่าไม่สามารถเข้าถึงได้ / ไม่ได้
- Static fence: fixed size OS
- Dynamic fence: fence register จะมี address ของ OS
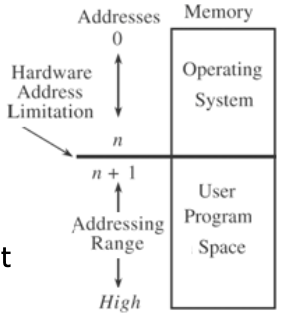 Fixed Fence
Fixed FenceFixed fence คือ address ที่ถูกกำหนดไว้ให้เก็บ OS และ users จะต้องเข้าไม่ถึง
- Base/bound register: Lower and upper address limit
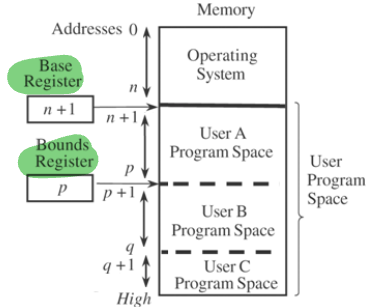 undefined
undefined- Segmentation: แบ่ง Memory ออกเป็น Logical units
- กำหนดสิทธิ์การ access ในแต่ละ segments
- OS จะเก็บตำแหน่ง physical address ไว้
- OS จะเก็บตำแหน่ง segment address ไว้ ด้วย <segment,offset>
- ข้อดี
- ข้อมูลทุกส่วนจะสามารถตรวจสอบได้
- สามารถตั้งสิทธิ์เข้าถึงที่แตกต่างกัน ในแต่ละ segments ได้
- users สามารถ share access ของ segments ได้
- ข้อเสีย
- จาก <segment,offset> OS ต้องรู้ขนาดของ segment ถึงจะ ยืนยัน access ได้ถูกต้อง
- ถ้าเป็นโปรแกรมที่มี Dynamic memory access ละ? OS จะต้องเก็บขนาดของ segments
- Memory fragmentation ช่องว่างใน segment
- ยุ่งยาก
- Paging: แบ่ง Memory ออกเป็น Logical units แต่จะมีขนาดที่เท่าๆ กัน (Fixed-size segments)
- OS จะเก็บตำแหน่ง paging address ไว้ ด้วย <paging,offset>
- ข้อดี
- ลดการเกิด Memory fragmentation
- OS ไม่จำเป็น ต้องเก็บขนาดของ variable segment
- ข้อเสีย
- No logical unity🌟 to pages: 1 โปรแกรมไม่ใช่ 1 segment
- จะให้สิทธิ์การเข้าถึงกับ page ได้ยังไง?
Control of Access to General Objects
- ต้องเช็คทุกการเข้าถึง
- ต้องให้สิทธิ์ที่น้อยที่สุดเสมอ
- สามารถเช็คการใช้งานได้
Protection Mechanism
- Directory
- เจ้าของไฟล์สามารถควบคุมการ Read, Write, Execute
- users แต่ละคนจะมี access rights directory
- ง่าย
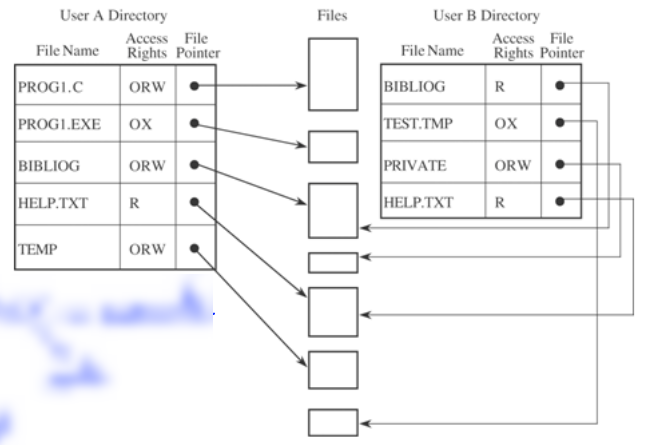 Access rights directory
Access rights directory- All-None Protection: สิทธิ์ default ของไฟล์ คือ public
- Group Protection
- user, group, world class (others)
- ง่่าย
- Perrsistent Permissions (สิทธิ์คงทน)
- ตั้งรหัส ให้ไฟล์
- Temporary Acquired Permission (สิทธิ์ชั่วคราว)
- ตั้ง set user id (suid)
- เช่นการคำสั่ง
passwdใน Linux จะเป็นการให้สิทธิ์ root กับ users ชั่วคราวเพื่อเปลี่ยนรหัส
UNIX File Access Control
- Set User Id (suid) หรือ Set Group Id (guid)
- สิทธิ์ชั่วคราว ของเข้าของไฟล์ ระหว่างที่ืเจ้าของไฟล์กำลังแก้ไขสิทธิ์
- Sticky bit
- ตัวกำหนดสิทธิ์ใน directory ให้ rename/move/delete
 UNIX File Access Control
UNIX File Access Control- superuser
- ข้อยกเว้น users จากสิทธิ์ปกติ
User Authentication
- การระบุตัวตน
- จะมี 2 ขั้นตอน
- Identification ระบุตัวตน
- Verification ยืนยันตัวตน
- จะระบุจากสิ่งที่บอกว่าเป็นเราจริงๆ
- จากสิ่งที่เรารู้ Password, PIN, etc.
- จากสิ่งที่เรามี Badge, Key, etc.
- จากสิ่งที่เราเป็น Biometrics
Password Guessing Steps เทคนิคการเดารหัส
- ไม่มีรหัส
- รหัสเหมือนกับ User Id
- รหัสมาจาก User Id
- คำศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษที่ใช้บ่อยๆ
- คำศัพท์ระดับวิทยาลัย (สั้นๆ)
- คำศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษทั้งหมด
- คำศัพท์ภาษาอื่นๆ ที่ใช้บ่อยๆ
- คำศัพท์ระดับวิทยาลัย (สั้นๆ) แต่เปลี่ยนตัวเล็กตัวใหญ่
PaSsWorDและการเปลี่ยน (เช่น 0 เป็น O) - คำศัพท์ภาษาอังกฤษทั้งหมด แต่เปลี่ยนตัวเล็กตัวใหญ่ และการเปลี่ยน
- คำศัพท์ภาษาอื่นๆ ที่ใช้บ่อยๆ แต่เปลี่ยนตัวเล็กตัวใหญ่ และการเปลี่ยน
- Brute force ตัวอักษร (ตัวเล็ก)
- Brute force ทุกตัว
Password Management
- Encryption
- Salt (UNIX)
- One-time passwords
UNIX Implementation
- จากเดิม
- รหัส 8 ตัวอักษร สร้าง 56-bit key
- 12-bit salt โดยใช้ DES Encryption เป็น One-way hash function
- ค่าถูกเข้ารหัส 25 ครั้ง
- Output ออกมาเป็นตัวอักษร 11 ตัว
- แบบใหม่
- ใช้ MD5 hash
- 48-bit salt
- Hash 1000 ครั้ง
- Output ออกมาเป็น 128-bit hash
Password Vulnerabilities
- Offline dictionary attack
- Specific account attack
- Popular password attack
- Password guessing against single user
- Workstation hijacking
- Exploiting user mistakes
- Exploiting multiple password use
- Electronic monitoring
Password Cracking
- Dictionary attacks
- Compare hashed word from dictionary to hashed file
- Rainbow table attacks
- Precompute tables of hash values for all salts
- Generates a large dictionary of possible passwords
- Precompute tables of hash values for all salts
Password File Access Control
- เพื่อป้องกันการ Password attack
- ป้องกันการ Offline quesing ด้วยการ denying access encrypted password
- ให้สิทธิ์เฉพาะ Privileged users
- ใช้รหัสที่ดีขึ้น รหัสที่สุ่ม
- เทคนิคการสร้างรหัสที่ดี
- ให้ความรู้ ในการสร้างรหัสที่ดี
- สุ่ม
- Reactive password checking ระบบจะรัน Password cracker เอง เพื่อตรวจสอบ
- Proactive password checking users จะเลือกรหัสทีระบบเช็คแล้วว่าใช้ได้เท่านั้น
Remote User Authentication
- จะติดปัญหาเรื่องการ ดักฟัง (eavesdropping) และ การส่งใหม่ (replay)
- Challenge-response protocol
- user จะส่ง Identity ให้ remote host
- host จะ generate number r เรียกว่า nonce (once-in-a-lifetime) และส่งให้ user หรือเรียกว่า challenge
- user จะส่ง hash ที่เข้ารหัสมากับ nonce
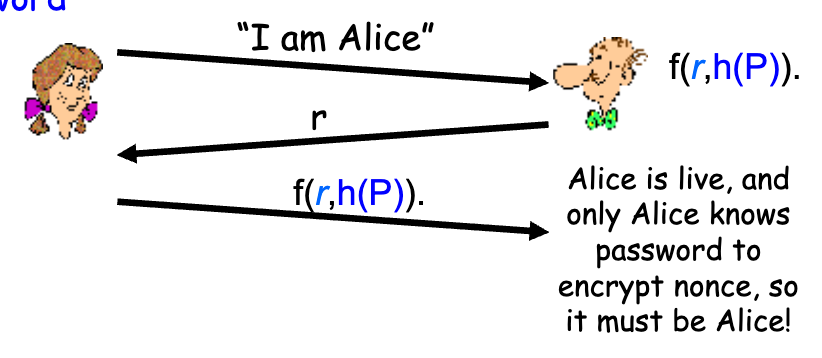 Challenge-response protocol
Challenge-response protocolOpenID Connect
- เป็น JSON-/REST-based identity protocol ที่สร้างมาจาก OAuth 2.0 กับ JWT protocol
- จะยื่นยันตัวตนด้วย Authorization server (Github, Google, Microsoft, …)
- End-user คนที่ต้องการระบุตัวเอง
- Relying party (RP) เว็บหรือ application ที่ต้องการจะระบุตัวตน
- OpenID provider (OP) คนที่จะมายืนยันตัวตน
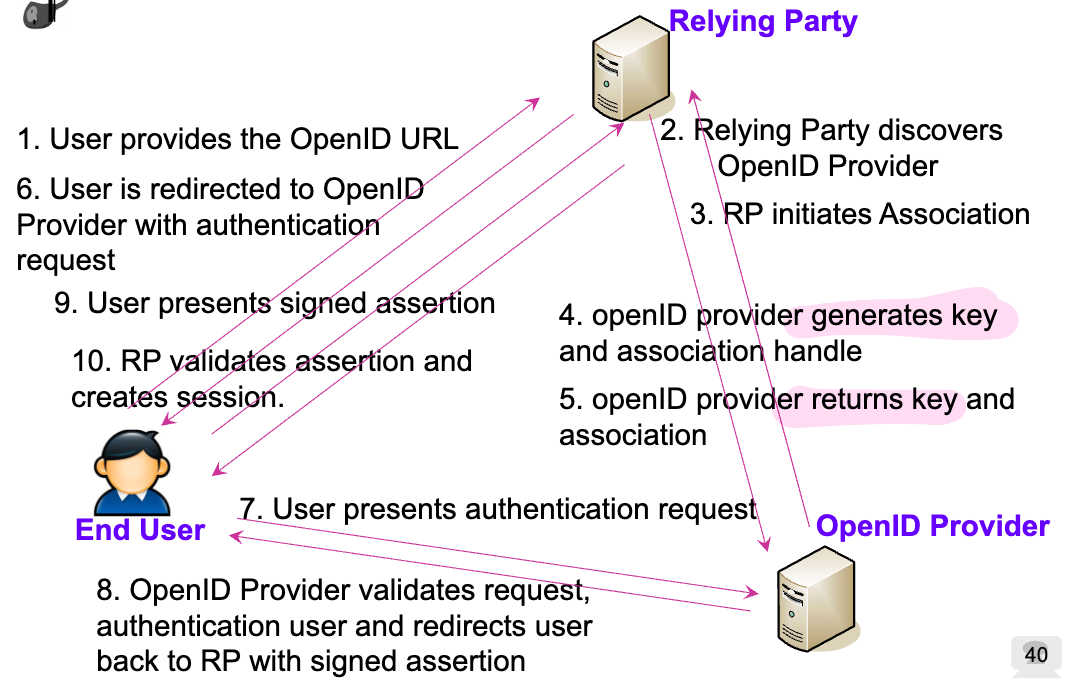 OpenID flow
OpenID flowAccess Control
- การควบคุมไม่ให้เกิดการใช้งานโดยไม่มีสิทธิ์ (unauthorized)
- มีการแบ่ง users และ groups
- คำศัพท์
- Authentication: พิสูตน์ตัวตน
- Authorization: การเช็คสิทธิ์
- Audit: การตรวจสอบกิจกรรมต่างๆ
Access Control Policies
Discretionary access control (DAC): ขึ้นอยู่กับเจ้าของข้อมูล
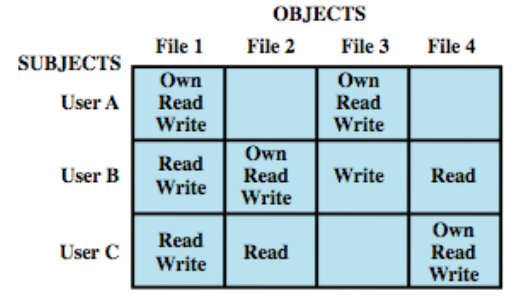 Access Matrix
Access Matrix- จะใช้ Access Matrix
- Subject จะใส่ใน rows
- Object จะใส่ใน columns
- จะใช้ Access Matrix
Mandatory access control (MAC): บังคับ
Role-based access control (RBAC): ขึ้นอยู่กับ Role
- จะใช้ Access Matric เหมือนกัน แต่จะมี Role matrix ด้วย
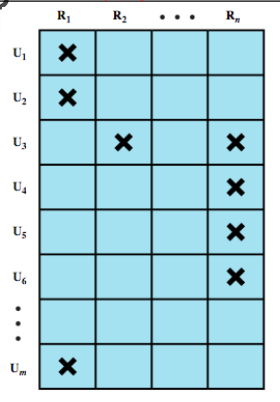 Role Matrix
Role Matrix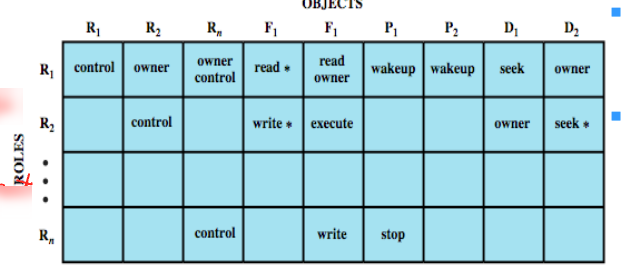 Role Access Matrix
Role Access Matrix- มี 4 Modesl
- RBAC: minimum functionality ของ RBAC
- RBAC: Role hierarchies, สามารถให้ role inherit permission จากอีก role ได้
- RBAC: Constraints เช่น Mutually exclusive roles, cardinality, prerequisite
- RBAC: ผสมระหว่าง RBACม RBACม RBAC
Acess Control Requirements
- Reliable input
- Support for fine and course specifications
- Least privilege
- Separation of duty: แยกขั้นตอนการทำงาน ชัดเจน
- Open & closed policies:
- Closed policy: อณุญาติให้เข้าถึงเฉพาะคนที่กำหนดเท่านั้น
- Open policy: อณุญาติให้เข้าถึงได้ทุกคน ยกเว้นคนที่กำหนดไว้
- Policy combination and conflict resolution: แก้ไขข้อขัดแย้ง
- Administrative policies
Access Control Elements
- Subject: คนที่จะเข้าถึงข้อมูล
- มักจะมี owner, group, world
- Object: ข้อมูล
- Access right: สิทธิ์ต่างๆ
- reat, write, execute, delete, create, search, …
Access Control Structures
- Access control lists (ACLs)
- ในแต่ละ Objects, ACLs จะมีรายชื่อของ users และสิทธิ์
- Capability Lists / Capability Tickets:
- ในแต่ละ Users, จะมีรายชื่อของ File และสิทธิ์
Trusted Operating System
- OS จะเชื่อถือได้ เพราะ
- Memory protection
- File protection
- General object access control
- User authentication
- 4 รากฐาน
- Policy: กฏ
- Model: representation ของกฏ
- Design: วิธีการสร้างโมเดล
- Trust: การรับประกันและความหน้าเชื่อถือ
Security Features of Ordinary OS
- Authentication of users
- Protection of memory
- File and I/O device access control
- Allocation and access control to general objects
- Enforcement of sharing
- Guarantee of fair service
- Inter-process communication and synchronization
- Protection of OS protection data
Security Features of Trusted OS
- User ID and authentication
- Mandatory access control (MAC)
- Discretionary access control (DAC)
- Object resue protection: OS จะต้องป้องกันการรั่วไหลข้อมูล
- Complete midation: ทุกการเข้าถึงข้อมูล มีการตรวจสอบ
- Trusted path: สร้างความมั่นใจให้กับ users กำลังสื่อสารกับคนที่กำลังสื่อสาร และจะไม่มีการดักฟัง หรือ แก้ไข
- Audit
- Audit log reduction
- Intrusion detection
Reference Monitor
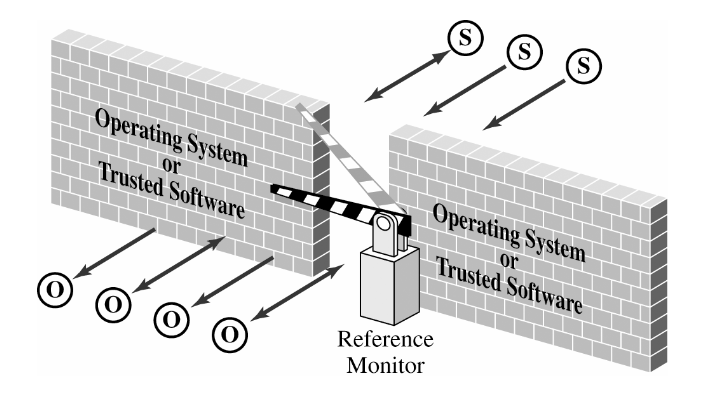 Reference Monitor
Reference Monitormade with ❤️ by @tonkaew131 Cookie policy